Too Many Mouldy Joints – Marijuana and Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis
Yousef Gargani1, Paul Bishop2 and David W. Denning1
Published: January 14, 2011
Received: December 30, 2010
Accepted: December 31, 2010
Medit J Hemat Infect Dis 2011, 3: e2011005 DOI 10.4084/MJHID.2011.005
This article is available from: http://www.mjhid.org/article/view/7054
Abstract
Marijuana is the most commonly used illicit substance in the UK and many other western countries, despite it being a class B drug. It is available legally in some localities, including the Netherlands. There is a well known link between marijuana use and schizophrenia. There is currently uncertainty about any causal association between marijuana use and lung cancer as the effects of concomitant tobacco smoking amongst these users confound analyses. A small number of cases of various forms of aspergillosis have been associated with marijuana smoking, but the association appears to be uncommon.[1-9]
We present 2 cases of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis (CPA) associated with extensive medicinal use of marijuana, and summarise the literature linking all forms of aspergillosis and marijuana use.
Case reports
Patient 1: A Caucasian male presented at the age of 47 with a right-sided pneumothorax (Figure 1), associated with pulmonary bullae. He had a four year history of progressive breathlessness. His tobacco smoking history was approximately 39 pack*years, but his breathlessness worsened considerably once he started to smoke marijuana (5 marijuana cigarettes (joints) daily) medicinally to alleviate rheumatoid arthritis-associated joint pain. On presentation, he reported coughing up thick sputum and experiencing some unexpected weight loss. His medications included a 5mg daily dose of prednisolone and 1g dose of sulfasalazine twice a day. His family history included one brother who had TB and another who had a pneumothorax.
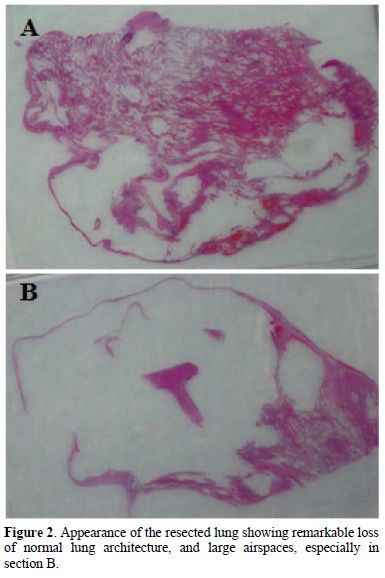
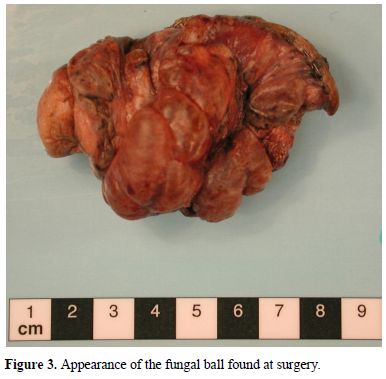
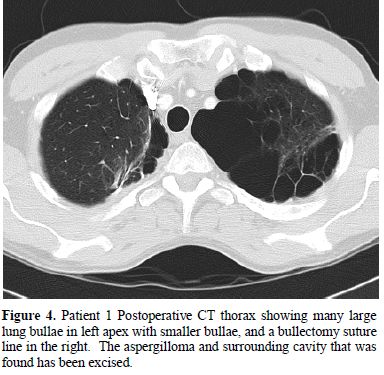
His pneumothorax did not resolve despite drainage; thus he underwent a right bullectomy and pleurectomy. One of the excised bullae (Figure 2) contained a pleural based abscess containing an aspergilloma (Figure 3). His CRP at this time was 333mg/l. Post-operatively his lung function failed to improve and a chest x-ray revealed that that his right lung remained abnormal, with cavitary changes. A CT scan showed severe emphysema with many large lung bullae especially in the left apex (Figure 4). His CRP normalised and his alpha 1 antitrypsin levels were normal.
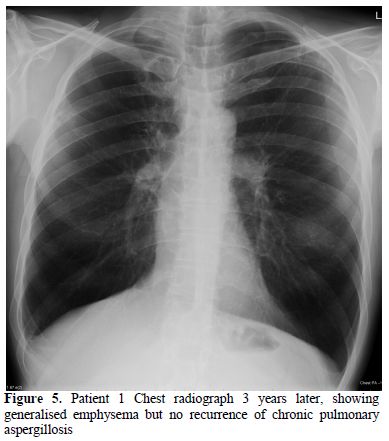
Pathological evidence of an aspergilloma with symptoms of weight loss and raised inflammatory markers is an indication for antifungal therapy. He was started on posaconazole 400mg bd and took it for 4 months. After treatment both his cough and sputum production improved and his Aspergillus fumigatus precipitin serum titre was 1:4. He stopped smoking marijuana. He was observed for recurrence of CPA for the following 4 years and there was no evidence of recurrence (Figure 5).
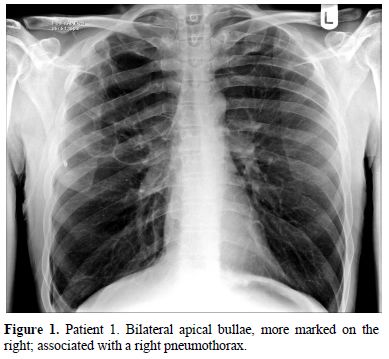
Figure 1. Patient 1. Bilateral apical bullae, more marked on the right; associated with a right pneumothorax.
Figure
3.
Appearance of the fungal ball found at surgery.
Figure 4. Patient 1 Postoperative CT
thorax showing many
large lung bullae in left apex with smaller bullae, and a bullectomy
suture
line in the right. The aspergilloma and surrounding cavity that was
found has
been excised.
Figure
5. Patient 1 Chest radiograph 3
years later, showing generalised emphysema but no recurrence of chronic
pulmonary aspergillosis
Patient 2: A 35 year-old Caucasian male presented with shortness of breath secondary to a viral infection. After investigations he was diagnosed with emphysema. He had been born with a Tetralogy of Fallot congenital heart malformation and underwent a surgical repair at the age of 10. Post-operatively he experienced immense pain and started smoking cannabis, without tobacco, to reduce it. He continued to grow his own marijuana and smoke several joints hospital aged 43, and then several times over the following two years, owing to type II respiratory failure. Aged 44, he stopped smoking cannabis,ending 34 years of smoking around 20 joints per day. Despitestopping smoking cannabis his respiratory function had diminished to such an extent that his exercise tolerance was only 10 yards on the flat. As a result he was started on long term oxygen therapy, requiring 3L continuously to maintain an oxygen saturation of 91%.
By 45 years his FEV1 was only 11% predicted and daily. He remained apparently well until admission to his FVC was 22% predicted. A CT scan revealed “severe pan-acinar emphysema involving the right upper and middle lobes; complex cavitary lesions in the left apex, one of which had the appearance of an aspergilloma” (Figure 7). Sputum culture revealed Aspergillus fumigatus. His Aspergillus precipitins titre was 1:8 and his Aspergillus IgG antibody level (Immunocap, Phadia) was 126mg/L. His total IgE was 180 and he had a positive Aspergillus RAST of 0.4, all consistent with chronic pulmonary aspergillosis. His respiratory function deteriorated such that he required a lung transplant; however the discovery of an aspergilloma was seen to be an absolute contraindication by the team treating him. He was started on voriconazole 200mg bd with some symptomatic improvement on therapeutic levels. However his lung function continued to deteriorate and 3 months later he died at the age of 46.
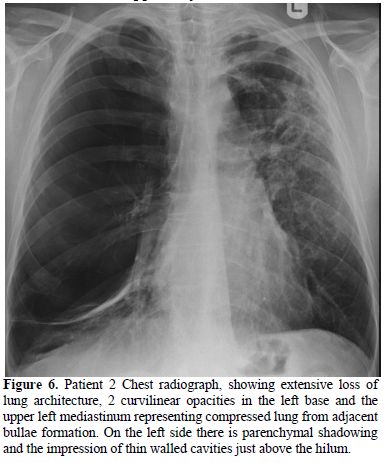
Figure 6. Patient 2 Chest radiograph, showing extensive loss of lung architecture, 2 curvilinear opacities in the left base and the upper left mediastinum representing compressed lung from adjacent bullae formation. On the left side there is parenchymal shadowing and the impression of thin walled cavities just above the hilum.
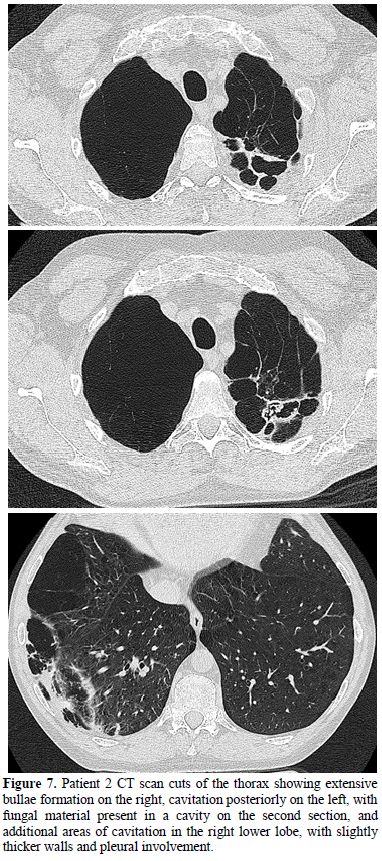
Figure
7.
Patient 2 CT scan cuts of the thorax showing extensive bullae formation
on the right,
cavitation posteriorly on the left, with fungal material present in a
cavity on
the second section, and additional areas of cavitation in the right
lower lobe,
with slightly thicker walls and pleural involvement.
Discussion
Aspergillus spp. are widespread and exposure to airborne conidia and hyphal fragments is universal. In humans who are immunocompromised these saprophytic fungi can cause life-threatening invasive aspergillosis and, in asthmatics and those with cystic fibrosis, allergic disease (allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA)). In those who have structural damage to their lungs but are apparently immunocompetent, Aspergillus can cause CPA, with or without an aspergilloma.
Invasive aspergillosis has been described in association with marijuana smoking in two cancer patients on chemotherapy,[1,2] two leukaemia patients,[3,4] a renal transplant recipient, [5] and a few patients with AIDS.[6] It is not recommended that patients undergoing chemotherapy or on substantial immunosuppression smoke marijuana, based on these observations. However the risk is not possible to quantify.
There have been two reported cases of ABPA associated with mouldy marijuana.[7,8] Given the frequency of asthma and ABPA, and the high frequency of marijuana usage amongst young people, these cases may represent a tiny proportion of those affected. This year, CPA was associated with marijuana smoking for the first time9 and we report here 2 additional cases. The previously reported patient died at just 34 years of age and patient 2 at 46 years of age. These high mortality rates of CPA have been described previously.[10-12]
The criteria for the diagnosis of CPA are the presence of pulmonary cavitation, with or without a fungal ball, in a non-immunocompromised patient with evidence of raised inflammatory markers and detectable circulating Aspergillus IgG antibodies (including Aspergillus precipitins).[13] The sensitivity of the IgG antibody tests is about 90%, with some discordance between assays. Occasional patients do not have detectable IgG antibody, but their Aspergillus IgE antibodies are raised and/or there are other data supporting the diagnosis, such as biopsy or culture evidence of infection. Patient 1 had histological evidence of infection with detectable Aspergillus precipitins. Patient 2 had a positive respiratory culture, with a fungal ball visible radiologically, and detectable Aspergillus IgG and IgE antibodies, as well as positive Aspergillus precipitins.
Both tobacco and marijuana are commonly contaminated with fungi, and serology from marijuana smokers exhibits evidence of Aspergillus exposure.[14] It remains to be seen whether fungal spores survive the burning process, indicating perhaps that exposure to Aspergillus comes from handling the marijuana rather than smoking it.[15] It has been observed that IA presents earlier after immunocompromise amongst smokers than non-smokers.[16]
The way marijuana is smoked is different to that of tobacco in that the cigarettes, or joints, are usually smoked without a filter and are smoked down to a smaller butt. Users hold their breath for longer and use the Valsalva manoeuvre. These measures maximise the diffusion of the psychoactive compounds. In doing so however, they expose their lungs to a greater tar and carbon monoxide burden, as well as subjecting their lungs to greater pressure changes. This barotrauma from marijuana smoking has long been associated with the formation of bullae and subsequent pneumothoraces. The association is so strong that some now recommend that patients presenting with spontaneous pneumothoraces should be directly questioned about marijuana smoking.[17]
The vast majority of marijuana is taken recreationally for its psychotropic effects. However, historically it has been used medicinally as an analgesic and an antiemetic. Even now, many people use marijuana purely for its medicinal benefits. It has been reported that 44% of US oncologists have recommended the illegal use of marijuana to their chemotherapy patients for iatrogenic nausea.[18] What must be borne in mind is that these patients are potentially severely immunosuppressed and therefore at risk of life-threatening IA.
Smoking marijuana affects the lungs structurally but may also affect them immunologically, by affecting alveolar macrophages.[19] This may predispose marijuana users to pulmonary infection. In our cases it is unknown whether the marijuana smoking caused the cavities which Aspergillus was able to colonise, or the marijuana was just the source of Aspergillus exposure and the Aspergillus caused the cavities. Research into the pathogenesis of both marijuana-related lung bullae and CPA are needed to proportionate causal blame in cases such as these.
Marijuana use has previously been implicated with the range of Aspergillus infections; the cases we present add aspergilloma and CPA to that list. In both cases marijuana was used for its medicinal benefits. With patient 1 smoking marijuana in combination with mild immunosuppression through low-dose steroids proved to be a potent combination. In patient 2 the heavy and prolonged marijuana usage in itself may have resulted in extensive pulmonary destruction and fatal CPA.
Together these cases highlight yet another potential risk associated with smoking marijuana. Understanding the full health burden presented by marijuana is hindered by a lack of disclosure by patients for fear of legal repercussions, coupled with poor history taking from clinicians; just 3% of daily marijuana smokers have their drug use documented in their clinical record.[20] More work is required to elucidate the full health burden of marijuana on those with pre-existing pathologies, so that governments, clinicians, and indeed users can make informed decisions about this controversial topic.
References
- Sutton S, Lum BL, Torti FM. Possible risk
of invasive aspergillosis with marijuana use during chemotherapy for
small cell lung cancer. Drug Intell Clinical Pharm 1986; 20: 289-91.
PMid:3009125.

- Cescon DW, Page AV, Richardson S, Moore MJ.
Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Associated with Marijuana Use in a Man
With Colorectal Cancer. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 2214-5. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.15.2777
PMid:18445848 .

- Hamadeh R, Ardehali A, Locksley RM, York
MK. Fatal Aspergillosis associated with smoking contaminated marijuana,
in a marrow transplant recipient. Chest 1988; 94: 432–3. doi:10.1378/chest.94.2.432
PMid:3293934.

- Szyper-Kravitz M, Lang R, Manor Y, Lahav M.
Early Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in a Leukemia Patient Linked to
Aspergillus Contaminated Marijuana Smoking. Leuk Lymphoma 2001; 42:
1433-7. doi:10.3109/10428190109097776 PMid:11911432.

- Marks WH, Florence L, Leiberman J, Chapman
P, Howard D, Roberts P et al. Successfully treated invasive
aspergillosis associated with smoking marijuana in a renal transplant
recipient. Transplantation 1996; 61: 1771-4. doi:10.1097/00007890-199606270-00018
PMid:8685958.

- Denning DW, Follansbee SE, Scolaro M,
Norris S, Edelstein H, Stevens DA. Pulmonary aspergillosis in the
acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. NEJM 1991; 324: 654-62. doi:10.1056/NEJM199103073241003
PMid:1994248.

- Llamas R, Hart DR, Schneider NS. Allergic
bronchopulmonary aspergillosis associated with smoking moldy marihuana.
Chest 1978; 73: 871-2. doi:10.1378/chest.73.6.871
PMid:657864.

- Kouevidjin G, Mazieres J, Fayas S, Didier A. Aggrevation of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosisby smoking marijuana. Revue Francias d’Allergologie et d’Immunologie Clinique 2003; 43: 192-4. doi:10.1016/S0335-7457(03)00050-9.
- Bal A, Agarwal AN, Das A, Suri Vikas, Varma
SC. Chronic necrotising pulmonary Aspergillosis in a marijuana addict:
a new cause of amyloidosis. Pathology 2010; 42: 197-200. doi:10.3109/00313020903493997
PMid:20085530.

- Jewkes, J, Kay, PH, Paneth, M, Citron, KM. Pulmonary aspergilloma: analysis of cavitating invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in immunocompromised patients. Ann Thorac Surg 1983; 53: 621.
- Tomlinson, JR, Sahn, SA. Aspergilloma in
sarcoid and tuberculosis. Chest 1987; 92:505. doi:10.1378/chest.92.3.505 PMid:3622028.

- Nam HS, Jeon K, Um SW, Suh GY, Chung MP,
Kim H, Kwon OJ, Koh WJ. Clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes
of chronic necrotizing pulmonary aspergillosis: a review of 43 cases.
Int J Infect Dis 2010;14:e479-82.

- Denning, DW, Riniotis, K, Dobrashian, R,
Sambatakou, H. Chronic cavitary and fibrosing pulmonary and pleural
aspergillosis: case series, proposed nomenclature change, and review.
Clin Infect Dis 2003; 37 Suppl 3:S265.

- Kagen SL, Kurup VP, Sohnle PG, Fink JN.
Marijuana smoking and fungal sensitization. J Allergy Clin Immunol
1983; 71: 389-93. doi:10.1016/0091-6749(83)90067-2..

- Verweij PE, Kerremans JJ, Voss A, Meis JF.
Fungal contamination of tobacco and marijuana. JAMA 2000; 284: 2875.
PMid:9311708.

- Singh N, Arnow PM, Bonham A, Dominguez E,
Paterson DL, Pankey GA et al. Invasive aspergillosis in liver
transplant recipients in the 1990s. Transplantation 1997; 64: 716-20. doi:10.1097/00007890-199709150-00009
PMid:15958866.

- Gill A. Bong Lung: Regular Smokers of
Cannabis Show Relatively Distinctive Histologic Changes That Predispose
to Pneumothorax. Am J Surg Pathol 2005; 29: 980-2. doi:10.1097/01.pas.0000157998.68800.cb.

- Doblin RE, Kleiman MA. Marijuana as
antiemetic medicine: a survey of oncologists’ experiences and
attitudes. J Clin Oncol 1991; 3: 1314-9. PMid:12412839.

- Tashkin DP, Baldwin GC, Sarafian T,
Dubinett S, Roth MD. Respiratory and immunologic consequences of
marijuana smoking. J Clin Pharmacol 2002; 42: 71S-81S.
PMid:8337854 PMCid:1311782.

- Polen MR, Sidney S, Tekawa IS, Sadler M,
Friedman GD. Health care use by frequent marijuana smokers who do not
smoke tobacco. West J Med 1993; 158: 596-601. PMid:11147983.